Textklassifikation in Python
Einführung
 Im vorigen Kapitel hatten wir die Formel zur Berechnung der Wahrscheinlichkeit hergleitet, dass ein
Document d in zu einer Klasse bzw. Kategorie c gehört, bezeichnet als P(c|d).
Im vorigen Kapitel hatten wir die Formel zur Berechnung der Wahrscheinlichkeit hergleitet, dass ein
Document d in zu einer Klasse bzw. Kategorie c gehört, bezeichnet als P(c|d).
Wir haben die Standardformel für P(c|d), so wie sie in verschiedenen wissenschaftlichen Abhandlungen verwendet wird1, in eine numerisch stabile Form gewandelt.
Für unsere Implementierung in Python benutzen wir einen auf "Naive Bayes" basierenden Klassifikator. Eine formale Einführung in das Konzept eines Naive-Bayes-Klassifikators befindet sich im vorigen Kapitel "Einführung in die Textklassifikation".
Python ist ideal für die Textklassifikation wegen seiner Stringklasse und deren mächtigen Methoden. Weiterhin werden mit dem Modul re leistungsstarke Tools zur Verfügung gestellt, die weit über den Rahmen anderer Programmiersprachen hinausgehen.
Die vorliegende Python-Implementierung eines Naive-Bayes-Klassifikators ist allerdings nicht auf Effizienz optimiert.
Python-Implementierung
Warnung: Die vorliegende Implementierung ist in Python 3 geschrieben und nicht Python 2.x kompatibel!Dokumenten-Repräsentation
Die Dokumente werden in unserer Implementierung nach dem sogenannten "bag of words"-Modell implementiert, was wir im folgenden Diagramm illustrieren: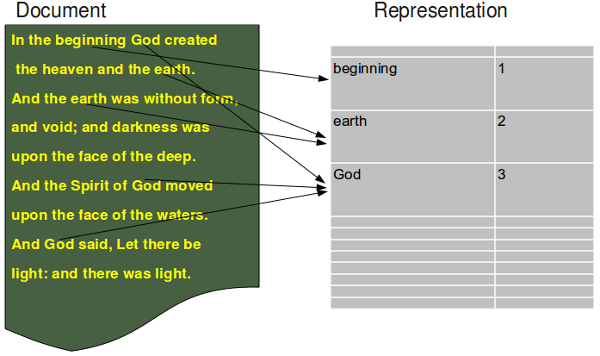
Benötigte Module
Unsere Implementierung benötigt das Modul re für reguläre Ausdrücke und die Betriebssystemschnittstelle im os-Modul:import re, os
BagOfWords-Klasse
class BagOfWords(object):
""" Implementing a bag of words, words corresponding with their frequency of usages in a "document"
for usage by the Document class, DocumentClass class and the Pool class."""
def __init__(self):
self.__number_of_words = 0
self.__bag_of_words = {}
def __add__(self,other):
""" Overloading of the "+" operator to join two BagOfWords """
erg = BagOfWords()
sum = erg.__bag_of_words
for key in self.__bag_of_words:
sum[key] = self.__bag_of_words[key]
if key in other.__bag_of_words:
sum[key] += other.__bag_of_words[key]
for key in other.__bag_of_words:
if key not in sum:
sum[key] = other.__bag_of_words[key]
return erg
def add_word(self,word):
""" A word is added in the dictionary __bag_of_words"""
self.__number_of_words += 1
if word in self.__bag_of_words:
self.__bag_of_words[word] += 1
else:
self.__bag_of_words[word] = 1
def len(self):
""" Returning the number of different words of an object """
return len(self.__bag_of_words)
def Words(self):
""" Returning a list of the words contained in the object """
return self.__bag_of_words.keys()
def BagOfWords(self):
""" Returning the dictionary, containing the words (keys) with their frequency (values)"""
return self.__bag_of_words
def WordFreq(self,word):
""" Returning the frequency of a word """
if word in self.__bag_of_words:
return self.__bag_of_words[word]
else:
return 0
Dokumenten-Klasse
class Document(object):
""" Used both for learning (training) documents and for testing documents. The optional parameter lear
has to be set to True, if a classificator should be trained. If it is a test document learn has to be set to False. """
_vocabulary = BagOfWords()
def __init__(self, vocabulary):
self.__name = ""
self.__document_class = None
self._words_and_freq = BagOfWords()
Document._vocabulary = vocabulary
def read_document(self,filename, learn=False):
""" A document is read. It is assumed, that the document is either encoded in utf-8 or in iso-8859... (latin-1).
The words of the document are stored in a Bag of Words, i.e. self._words_and_freq = BagOfWords() """
try:
text = open(filename,"r", encoding='utf-8').read()
except UnicodeDecodeError:
text = open(filename,"r", encoding='latin-1').read()
text = text.lower()
words = re.split("[^\wäöüÄÖÜß]*",text)
self._number_of_words = 0
for word in words:
self._words_and_freq.add_word(word)
if learn:
Document._vocabulary.add_word(word)
def __add__(self,other):
""" Overloading the "+" operator. Adding two documents consists in adding the BagOfWords of the Documents """
res = Document(Document._vocabulary)
res._words_and_freq = self._words_and_freq + other._words_and_freq
return res
def vocabulary_length(self):
""" Returning the length of the vocabulary """
return len(Document._vocabulary)
def WordsAndFreq(self):
""" Returning the dictionary, containing the words (keys) with their frequency (values) as contained
in the BagOfWords attribute of the document"""
return self._words_and_freq.BagOfWords()
def Words(self):
""" Returning the words of the Document object """
d = self._words_and_freq.BagOfWords()
return d.keys()
def WordFreq(self,word):
""" Returning the number of times the word "word" appeared in the document """
bow = self._words_and_freq.BagOfWords()
if word in bow:
return bow[word]
else:
return 0
def __and__(self, other):
""" Intersection of two documents. A list of words occuring in both documents is returned """
intersection = []
words1 = self.Words()
for word in other.Words():
if word in words1:
intersection += [word]
return intersection
Die Klasse DocumentClass
Die Klasse DocumentClass ist die Klasse für unser Dokumentenklassen. Sie erbt von der Klasse Document.
class DocumentClass(Document):
def __init__(self, vocabulary):
Document.__init__(self, vocabulary)
self._number_of_docs = 0
def Probability(self,word):
""" returns the probabilty of the word "word" given the class "self" """
voc_len = Document._vocabulary.len()
SumN = 0
for i in range(voc_len):
SumN = DocumentClass._vocabulary.WordFreq(word)
N = self._words_and_freq.WordFreq(word)
erg = 1 + N
erg /= voc_len + SumN
return erg
def __add__(self,other):
""" Overloading the "+" operator. Adding two DocumentClass objects consists in adding the
BagOfWords of the DocumentClass objectss """
res = DocumentClass(self._vocabulary)
res._words_and_freq = self._words_and_freq + other._words_and_freq
return res
def SetNumberOfDocs(self, number):
self._number_of_docs = number
def NumberOfDocuments(self):
return self._number_of_docs
Die Pool-Klasse
Die Klasse pool ist die Klasse, in der die Dokumentenklassen gelernt werden, und die die Klassifikationsmethoden zur Verfügung stellt:
class Pool(object):
def __init__(self):
self.__document_classes = {}
self.__vocabulary = BagOfWords()
def sum_words_in_class(self, dclass):
""" The number of times all different words of a dclass appear in a class """
sum = 0
for word in self.__vocabulary.Words():
WaF = self.__document_classes[dclass].WordsAndFreq()
if word in WaF:
sum += WaF[word]
return sum
def learn(self, directory, dclass_name):
""" directory is a path, where the files of the class with the name dclass_name can be found """
x = DocumentClass(self.__vocabulary)
dir = os.listdir(directory)
for file in dir:
d = Document(self.__vocabulary)
print(directory + "/" + file)
d.read_document(directory + "/" + file, learn = True)
x = x + d
self.__document_classes[dclass_name] = x
x.SetNumberOfDocs(len(dir))
def Probability(self, doc, dclass = ""):
"""Calculates the probability for a class dclass given a document doc"""
if dclass:
sum_dclass = self.sum_words_in_class(dclass)
prob = 0
d = Document(self.__vocabulary)
d.read_document(doc)
for j in self.__document_classes:
sum_j = self.sum_words_in_class(j)
prod = 1
for i in d.Words():
wf_dclass = 1 + self.__document_classes[dclass].WordFreq(i)
wf = 1 + self.__document_classes[j].WordFreq(i)
r = wf * sum_dclass / (wf_dclass * sum_j)
prod *= r
prob += prod * self.__document_classes[j].NumberOfDocuments() / self.__document_classes[dclass].NumberOfDocuments()
if prob != 0:
return 1 / prob
else:
return -1
else:
prob_list = []
for dclass in self.__document_classes:
prob = self.Probability(doc, dclass)
prob_list.append([dclass,prob])
prob_list.sort(key = lambda x: x[1], reverse = True)
return prob_list
def DocumentIntersectionWithClasses(self, doc_name):
res = [doc_name]
for dc in self.__document_classes:
d = Document(self.__vocabulary)
d.read_document(doc_name, learn=False)
o = self.__document_classes[dc] & d
intersection_ratio = len(o) / len(d.Words())
res += (dc, intersection_ratio)
return res
Benutzung des Klassifikators
Damit Sie einen Klassifikator lernen und testen können, stellen wir einen ein "Lern und Testset zum Download" zur Verfügung. Dabei handelt es sich um sechs Klassen mit englischen Witzen der Rubriken "clinton", "lawyer", "math", "medical", "music", "sex".
from NaiveBayes import Pool
import os
DClasses = ["clinton", "lawyer", "math", "medical", "music", "sex"]
base = "../learn/"
p = Pool()
for i in DClasses:
p.learn(base + i, i)
base = "../test/"
for i in DClasses:
dir = os.listdir(base + i)
for file in dir:
res = p.Probability(base + i + "/" + file)
print(i + ": " + file + ": " + str(res))
Fußnoten:
1 Weitergehende Artikel finden sich im Abschnitt "Weiterführende Literatur" des vorigen Kapitels von unserem Python-Kurs.


 Buch kaufen
Buch kaufen
 Buch kaufen
Buch kaufen
 Buch kaufen
Buch kaufen

